Autonomous Stack Integration with ROS
ROS를 이용하여 Autonomous Stack을 Integration 해보자
2021-10-04 10:10
Autonomous Integration Project: Step1
AUTHOR: Sungwook LE
DATE: ‘21.10/4 Lecture: System Integration, Udacity
My Repo: Here
ROS WIKI: Here ROS 용어: Here 국문 메뉴얼: Here
1. Introduction
- Autonomous Full-Stack 이란?
- 자율주행 SW에서
인지(Perception), 판단(Decision), 측위(Localization), 지도(Mapping), 계획(Planning), 제어(Control) 등Fully Autonomous Vehicle 구현을 위해 필요한 기술(기능) 전체를 말하는 것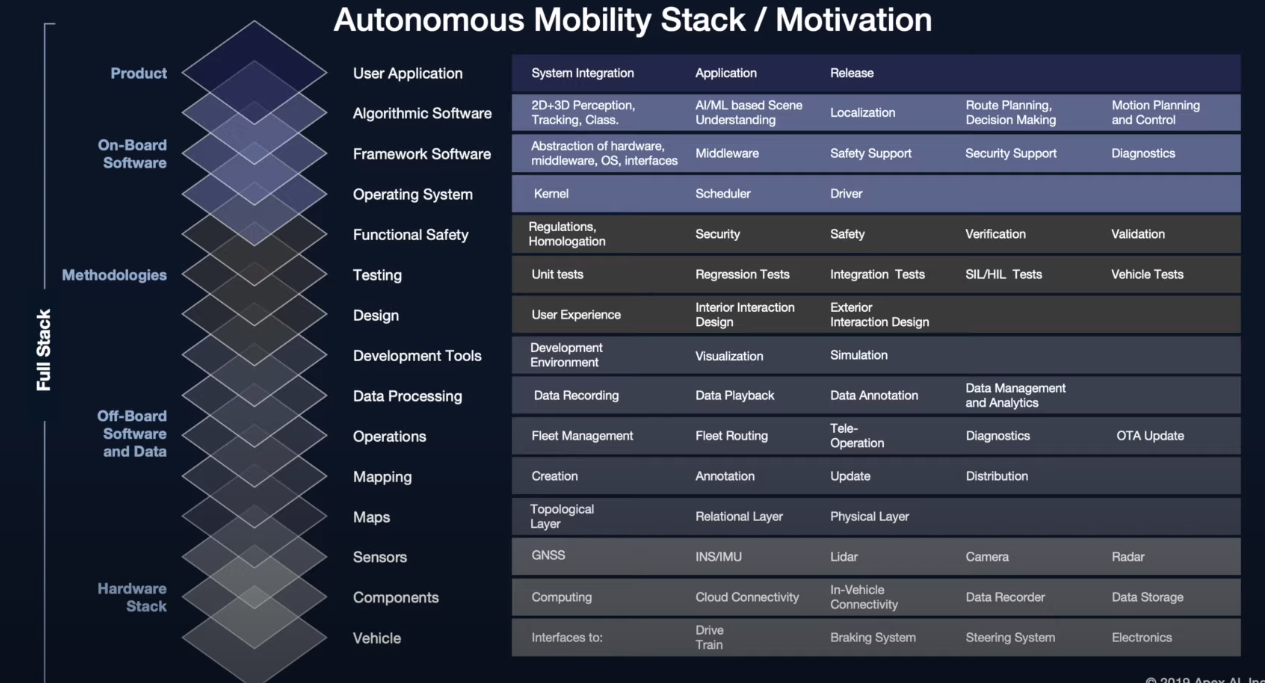
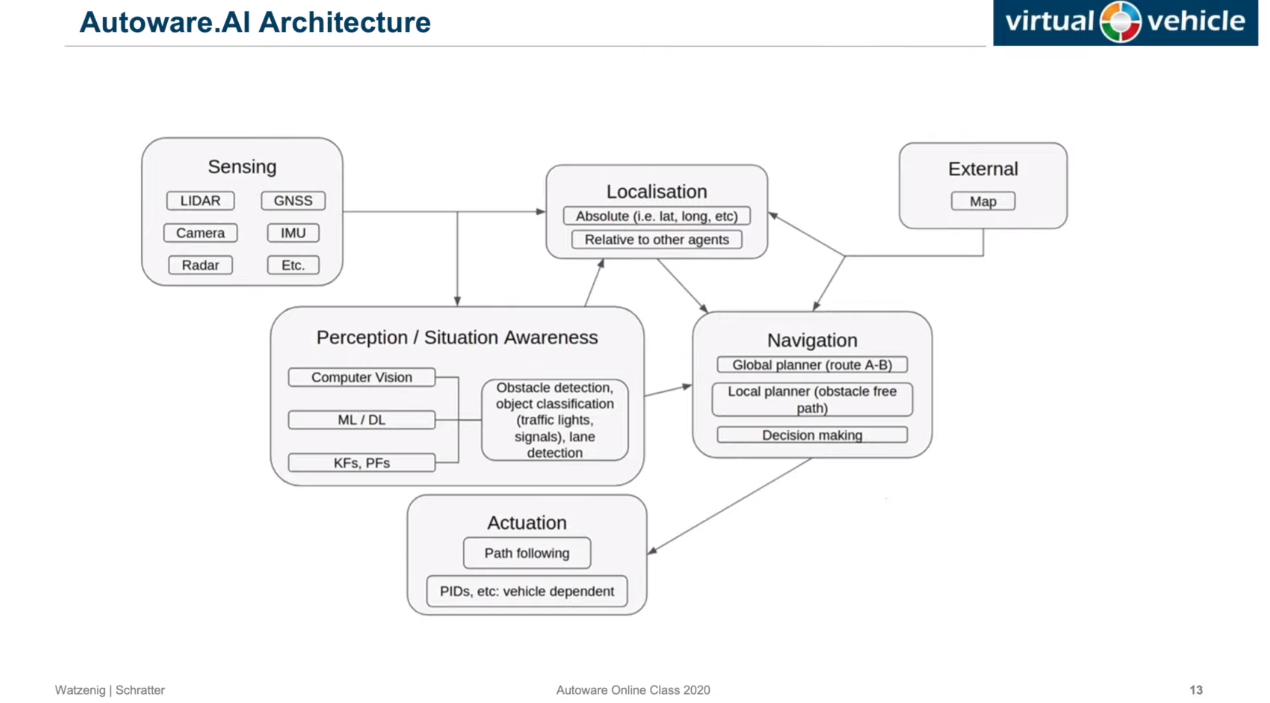
- ROS와 같은
Operating System위에서Framework의 형태로 모듈/독립성을 가진 여러 기능SW의Stack으로 자율주행이 구성된다는 의미(목표)에서 사용되는 단어
- 자율주행 SW에서
ROS를 이용하여 기능 Stack을Node/Pkg단위로 쌓아보는 것이 이번 포스팅의 목표이다.
2. ROS Basic
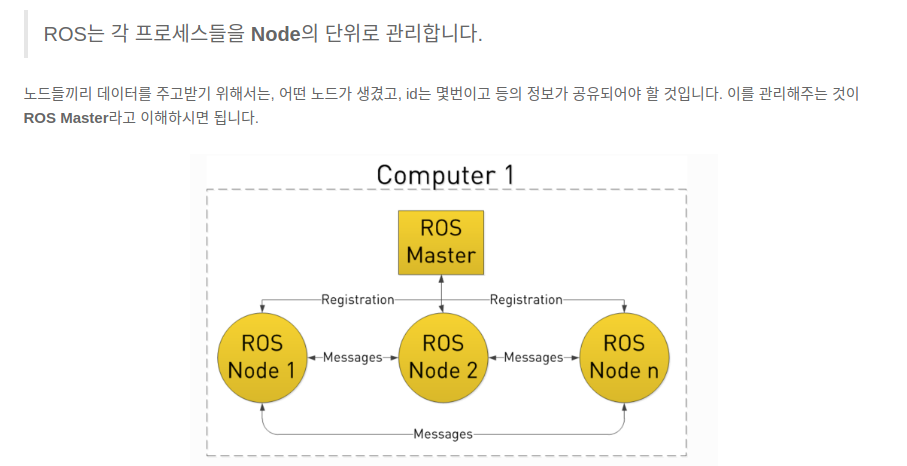
-
ROS명령어 (용어 설명)
1.roscore:rosmaster를 시작하는 명령어로 roscore가ros master가 된다. rosmaster가node를 하나로 묶어주는 역할을 한다.roscore
2.rosrun:node를 생성시키는 명령어로, pkg가 roscore에 위치하게 된다. 다시 말해,roscore가 실행된 이후에 그 아래에node를 실행시키는 명령어 이다.rosrun pkg이름 code
3.rospack: 패키지란 로스를 구성하는 기본 단위로써 실행 가능한 노드를 포함하고 있다. 로스는 패키지를 단위로 각각의 응용 프로그램들이 개발된다. 패키지는 최소한 하나 이상의 노드를 포함하고 있다.
4.roslaunch: 여러개의node를 하나하나rosrun할 필요 없이launch파일을 작성하여roslaunch로 동시에 실행 가능함

5.rosnode: 독립적으로 topic을 주고 받는 기능 모듈이node이다. 기능 stack을 하나의node에 구현할 수 있고, 이러한node를 여러개 쌓음으로써, 전체 시스템을 구성하자는 것이 ROS의 목표이다.
6.rostopic:node끼리sub, pub하는topic을 의미한다. 예를 들어, 하나의 node는 여러개의 node로 부터 여러개의 topic을sub하고 알고리즘을 수행하여pub하는 형태로 여러node와 인터페이싱하게 된다. 이 때,rostopic echo 토픽을 통해 ros 안에서node간pub, sub하는 topic을 터미널 창에서 볼 수 있다.
7.rosmsg:topic을 타고 흐르는node간의 소통 매개체- etc.
rostopic list: pub,sub 되고 있는topic들의 list를 보여줌 - etc.
rosnode list: node info 알려줌 - etc.
rostopic info xxxx:xxxxtopic의 information을 알려줌. 예를 들면Type: styx_msgs/Lane - etc.
rosmsg info styx_msgs/Lane:styx_msgs/Lane의 msg 구조를 알려줌 - etc.
rospy.loginfo등 로그 메시지 ROS.org
- etc.
-
node를 구동시키는 방식
1. rate(x) 주기 작동
-rospy.rate(x)를 사용하여 node가 sampling rate를 가지고 반복 작동하게 하는 방식으로,rate.sleep()과 같이 쓴다.
2. spin() call back 작동
-rospy.spin()은 topic이subs되면callback함수를 이용하여 node가 작동되게 하는 방식이다. - 두개의 방식은 하나의node에서 같이 써도 된다.
3. 사용 예시class ROS_NODE(object): def __init__(self): self.pub = rospy.Publisher('/mode', topic_msg, queue_size=1) # call_back 함수, subs가 들어와야 작동 rospy.Subscriber('/node', topic_msg, self.call_back) rospy.spin() # 또는 주기 함수 self.loop() def loop(self): rate = rospy.Rate(50) while not rospy.is_shutdown(): # 알고리즘, 주기적으로 작동 publish() rate.sleep() def publish(self): msg = topic_msg() self.pub.publish(msg)
3. Project Brief
- Udacity의 ROS를 이용한 System Integration 프로젝트 리뷰
- Including Stack:
traffic light detection,control, andwaypoint following- Code Structure

- Code Structure
docker를 이용하여 진행하였기 때문에, 실행을 위하여 아래의 명령어를 사용하여docker해야한다.docker run -p 4567:4567 -v $PWD:/capstone -v /tmp/log:/root/.ros/ --rm -it capstonedocker가 돌아가면,docker ps // 돌아가고 있는 도커 리스트 체크 docker stop [id] // 도커 실행 해제 docker exec -it [134adb2ba12 혹은 my-container] /bin/bash- 구현 코드는
repository를 참고하길 바라고, 빠른 리마인드를 목적으로DBW_Node코드를 살펴보자
import rospy
from std_msgs.msg import Bool
from dbw_mkz_msgs.msg import ThrottleCmd, SteeringCmd, BrakeCmd, SteeringReport
from geometry_msgs.msg import TwistStamped
import math
from twist_controller import Controller
class DBWNode(object):
def __init__(self):
rospy.init_node('dbw_node')
# get parameter from server, the number (2nd argu) is default value
vehicle_mass = rospy.get_param('~vehicle_mass', 1736.35)
fuel_capacity = rospy.get_param('~fuel_capacity', 13.5)
brake_deadband = rospy.get_param('~brake_deadband', .1)
decel_limit = rospy.get_param('~decel_limit', -5)
accel_limit = rospy.get_param('~accel_limit', 1.)
wheel_radius = rospy.get_param('~wheel_radius', 0.2413)
wheel_base = rospy.get_param('~wheel_base', 2.8498)
steer_ratio = rospy.get_param('~steer_ratio', 14.8)
max_lat_accel = rospy.get_param('~max_lat_accel', 3.)
max_steer_angle = rospy.get_param('~max_steer_angle', 8.)
self.steer_pub = rospy.Publisher('/vehicle/steering_cmd',
SteeringCmd, queue_size=1)
self.throttle_pub = rospy.Publisher('/vehicle/throttle_cmd',
ThrottleCmd, queue_size=1)
self.brake_pub = rospy.Publisher('/vehicle/brake_cmd',
BrakeCmd, queue_size=1)
self.controller = Controller(vehicle_mass, fuel_capacity, brake_deadband, decel_limit,
accel_limit, wheel_radius, wheel_base, steer_ratio, max_lat_accel, max_steer_angle)
rospy.Subscriber('/vehicle/dbw_enabled', Bool, self.dbw_enabled_cb)
rospy.Subscriber('/twist_cmd', TwistStamped, self.twist_cb)
rospy.Subscriber('/current_velocity', TwistStamped, self.velocity_cb)
self.current_vel = None
self.curr_ang_vel = None
self.dbw_enabled = None
self.linear_vel = None
self.angular_vel = None
self.throttle = self.steering = self.brake = 0
self.loop()
rospy.spin()
def loop(self):
rate = rospy.Rate(50) # 50Hz
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
if not None in (self.current_vel, self.linear_vel, self.angular_vel):
self.throttle, self.brake, self.steering = self.controller.control(self.current_vel,
self.dbw_enabled,
self.linear_vel,
self.angular_vel)
if self.dbw_enabled:
#rospy.logwarn("angular_vel: {:10f}".format(self.angular_vel))
self.publish(self.throttle, self.brake, self.steering)
rate.sleep()
def dbw_enabled_cb(self, msg):
self.dbw_enabled = msg
def twist_cb(self, msg):
self.linear_vel = msg.twist.linear.x
self.angular_vel = msg.twist.angular.z
def velocity_cb(self, msg):
self.current_vel = msg.twist.linear.x
def publish(self, throttle, brake, steer):
tcmd = ThrottleCmd()
tcmd.enable = True
tcmd.pedal_cmd_type = ThrottleCmd.CMD_PERCENT
tcmd.pedal_cmd = throttle
self.throttle_pub.publish(tcmd)
scmd = SteeringCmd()
scmd.enable = True
scmd.steering_wheel_angle_cmd = steer
self.steer_pub.publish(scmd)
bcmd = BrakeCmd()
bcmd.enable = True
bcmd.pedal_cmd_type = BrakeCmd.CMD_TORQUE
bcmd.pedal_cmd = brake
self.brake_pub.publish(bcmd)
if __name__ == '__main__':
DBWNode()
rosrun/launch되면dbw_node가 생성 된다.rosmaster아래에서 독립적으로node는 계속적으로 작동하게 된다.def __init__(self)에서 모든 작동 flow를 확인할 수 있다.class의method들은__init__에서 쓰여진 바와 같이 사용된다.
4. 결론
ROS는Node간 메세지 교환 방식으로 프로그램을 잘게 나누어 공동으로 개발 가능하다는 것이 큰 장점이다.- 자율주행 stack을 직접 나누어 구현하기 편하고,
library, package를 제공해줌으로서, sensor 등의hw를 쉽게 이식해 올 수 있다. ros에서 제공하는 개발지원tool도 빼 놓을 수 없는 장점이다.ros1에서는 roscore에 묶여서 하나의 네트워크 채널로 실행되면서 실시간성 보장이 어려운 문제가 있었으나,ros2에서는 많이 개선된 듯 하다.- 단점을 하나 보태자면, 단일 로봇을 위한 os로서 군집 로봇에는 한계가 있는 듯 하다.
